The GEBCO bathymetric grid is accompanied by a Type Identifier (TID) Grid, the function of which is to identifier the source data type that the corresponding grid cell in the bathymetric grid is based on.
The aim is to allow users to assess the ‘quality’ of the grid in a particular area, i.e. if it is based on multibeam data, singlebeam data or on interpolation, etc.
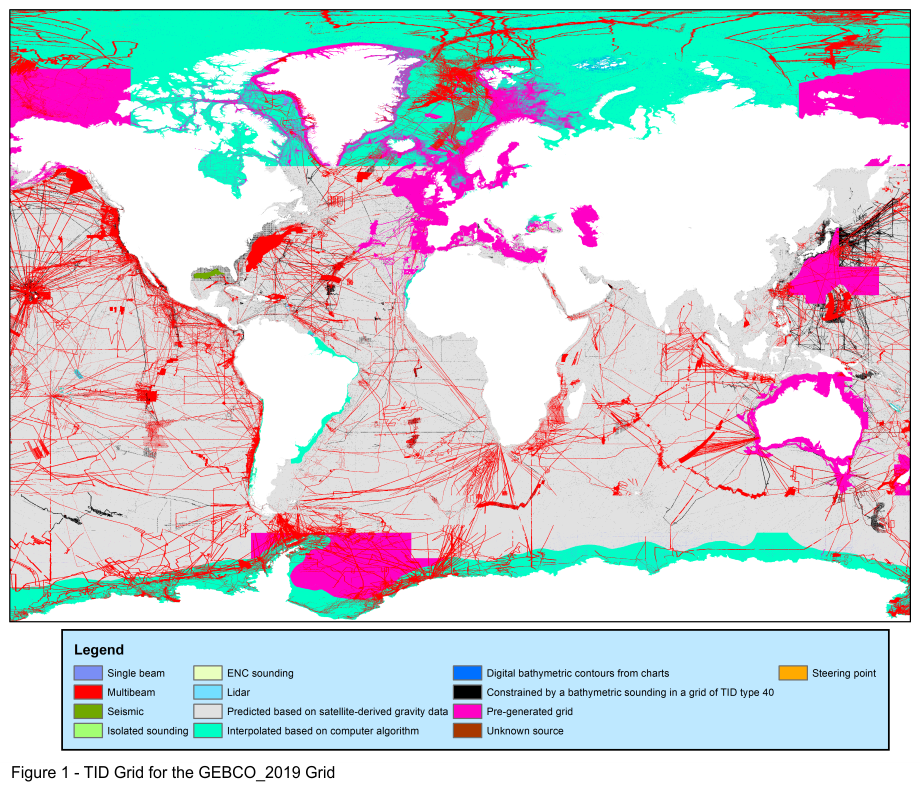
The above image shows the TID grid coverage, colour-coded for TID value for the GEBCO_2019 Grid.
The following images show examples of how the TID Grid can be used to highlight the types of data that areas of the GEBCO grid are based on.
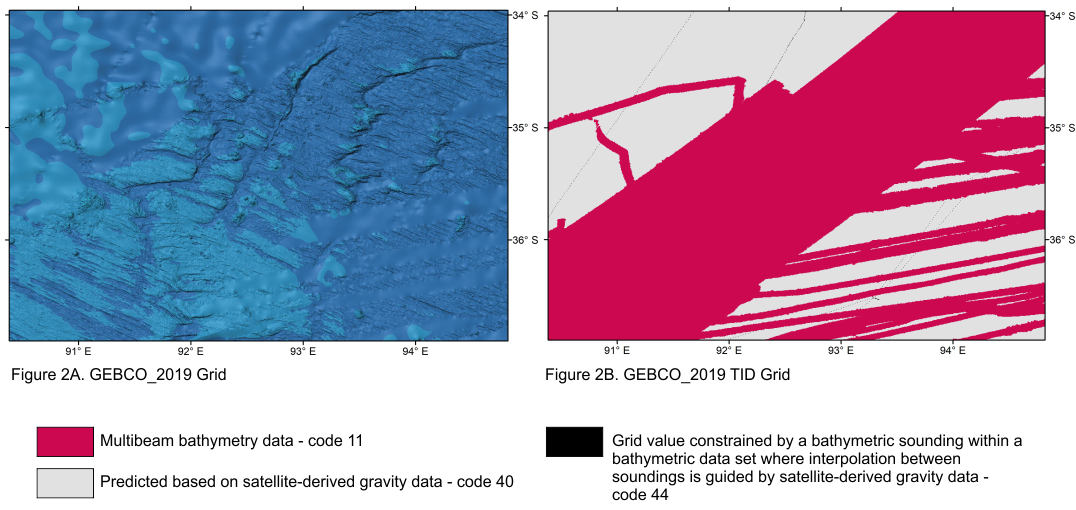
Figure 2A shows a section of the GEBCO grid. The region in the upper left of the image is based on a database of soundings with interpolation between them guided by satellite-derived gravity data (the base grid), while in the centre and lower right it is based on multibeam data.This difference in data source is reflected in the level of detail shown in the bathymetric grid. Figure 2B shows the TID grid for this area and the coverage of the various types of data used to generate the GEBCO grid in this region. This helps to highlight the areas that are based on measured data and those that are based on interpolation.
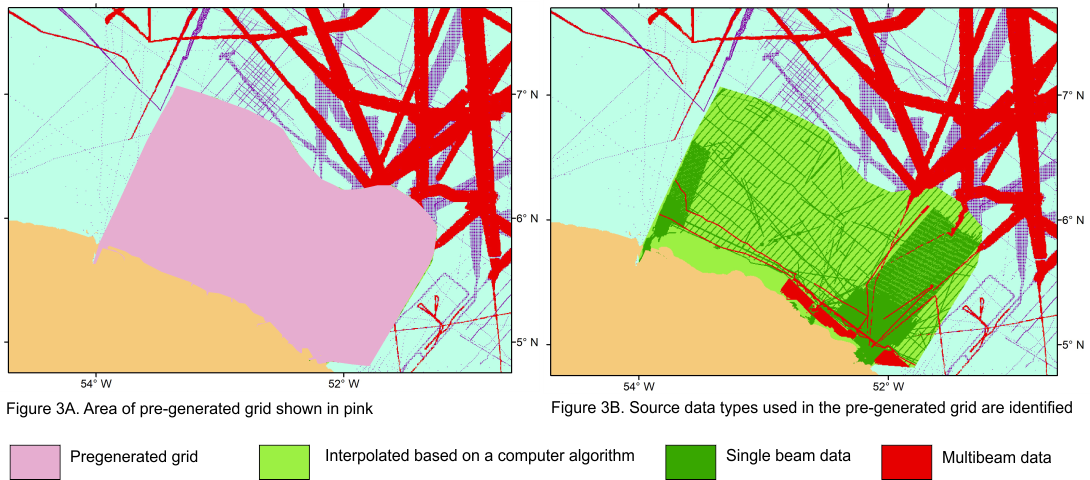
In Figure 3A the area shown in pink is a region of the GEBCO Grid based on a pre-generated grid, i.e. a grid that has been generated from multiple data sources. It is not possible to distinguish between the different source data types and the areas based on interpolation. It may appear that the whole region is mapped.
In Figure 2B, the individual source data sets are now coded for their data type. This makes it possible to identify regions based on multibeam and single beam data and those based on interpolation.
Find out more about the TID grid and how it can be generated from Chapter 17 of the GEBCO Cook Book.
The table below details the coding of the GEBCO Type Identifier (TID) grid.
| TID | Definition |
|---|---|
| 0 | Land |
| Direct measurements | |
| 10 | Singlebeam - depth value collected by a single beam echo-sounder |
| 11 | Multibeam - depth value collected by a multibeam echo-sounder |
| 12 | Seismic - depth value collected by seismic methods |
| 13 | Isolated sounding - depth value that is not part of a regular survey or trackline |
| 14 | ENC sounding - depth value extracted from an Electronic Navigation Chart (ENC) |
| 15 | Lidar - depth derived from a bathymetric lidar sensor |
| 16 | Depth measured by optical light sensor |
| 17 | Combination of direct measurement methods |
| Indirect measurements | |
| 40 | Predicted based on satellite-derived gravity data - depth value is an interpolated value guided by satellite-derived gravity data |
| 41 | Interpolated based on a computer algorithm - depth value is an interpolated value based on a computer algorithm (e.g. Generic Mapping Tools) |
| 42 | Digital bathymetric contours from charts - depth value taken from a bathymetric contour data set |
| 43 | Digital bathymetric contours from ENCs - depth value taken from bathymetric contours from an Electronic Navigation Chart (ENC) |
| 44 | Bathymetric sounding - depth value at this location is constrained by bathymetric sounding(s) within a gridded data set where interpolation between sounding points is guided by satellite-derived gravity data |
| 45 | Predicted based on helicopter/flight-derived gravity data |
| 46 | Depth estimated by calculating the draft of a grounded iceberg using satellite-derived freeboard measurement. |
| Unknown | |
| 70 | Pre-generated grid - depth value is taken from a pre-generated grid that is based on mixed source data types, e.g. single beam, multibeam, interpolation etc. |
| 71 | Unknown source - depth value from an unknown source |
| 72 | Steering points - depth value used to constrain the grid in areas of poor data coverage |